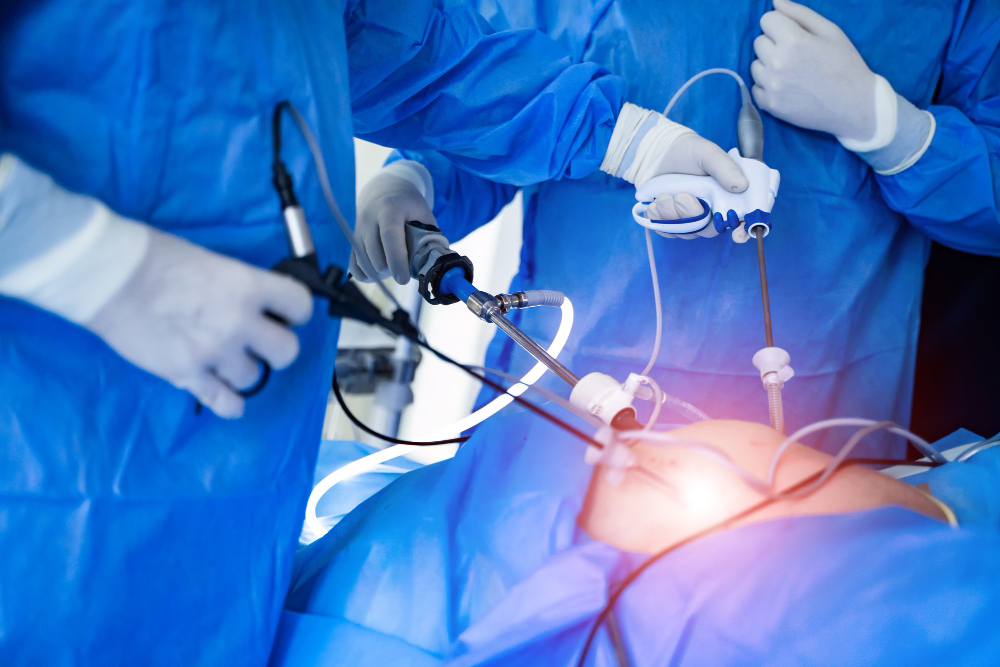
Surgery is a branch of clinical medicine that deals with the treatment of diseases and injuries in an operative manner.
The name “surgery” comes from the Greek word “Chirurgia”, which means hand and work, which literally explains the need for a precise, skillful, and experienced surgical hand for a successful operation.
In order for the surgeon to perform his work successfully and accurately, it is necessary to have a broad medical education, as well as knowledge of the technique and technology.
Which operations are performed most often?
– Bile Calculosis Surgery
Gallstones are formed by the deposition of their contents, cholesterol, and bilirubin. They vary in size from very small (1-2mm) that look like sand to very large that fill the entire gallbladder and have their shape. Often there is a mixture of all sizes in the patient.
The pebbles in h. bags are present in 20-30% of the population and are more common in females, the ratio is 4: 1. In some cases, the small stones give the impression of bile and never form a stone. Symptoms are: pain under the right costal arch and spoon and may spread to the right shoulder blade, nausea, and vomiting. In some cases, in the case of small calculus, a stone may enter the main bile duct, obstructing bile flow, in which case the patient’s first symptom is yellowing of the skin and visible mucous membranes, followed by fever and white feces. In that case, it is a complication of the disease. The standard method for proving biliary calculi is abdominal ECHO. In some cases, when the surgeon evaluates, it is necessary to make more complex diagnostic tests – ERCP and MRCP. Gall calculus, unfortunately, is exclusively a surgical disease (it can be treated only with surgery). The standard method of surgical treatment anywhere in the world is the laparoscopic method, popularly known as “four-hole surgery”. The type of anesthesia is always general. With this operation, the patient does not have an incision as before, thus excluding the possibility of ventral hernias at the site of surgery, the duration of the operation is shortened, the need for antibiotics and pain medications is less, and the amount of drugs in anesthesia is reduced, postoperative pain is drastically reduced, the patient is rapidly mobilized and rapidly switches to fluid and food intake through the mouth. The rehabilitation of the patient is much faster, the ability to work is possible after a week. Simultaneously with the laparoscopic method, it is possible to examine the other organs in the abdomen and possibly their surgical treatment, ie. “Two operations in one”.
– Surgery of hernias of the anterior abdomen or popularly known as hernia or brunch, occurs as a combination of increased intra-abdominal pressure (when lifting heavy objects, constipation, prolonged coughing and sneezing, tumors, heart failure, etc.) and opening or weakness of musculature or fascia where increased pressure pushes organs and tissues through the weak point of the wall.
Muscle weakness can be congenital but usually occurs later in life. Depending on where they occur, we distinguish inguinal, femoral, umbilical, epigastric, and extremely rare Spiegel hernia. A special group includes ventral or incisional hernias, which occur at the site of a previous abdominal operation.
Hernia knows no age limit, it occurs in both men and women. It is manifested by the appearance of painless or slightly sensitive swelling of the skin of the abdomen, which usually occurs after physical exertion and disappears when the patient is in a supine position.
Evolutionarily, as time goes on, the hernia increases in size. Extremely in childhood, it can happen that with the development of the muscle wall, those weak points are strengthened naturally. Therefore, surgical treatment can be expected in children.
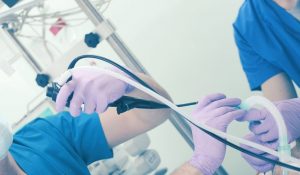
What is open surgery?
This is the main traditional procedure. Here, the doctor makes a large incision to replace or repair tissue or an organ in the body. The surgeon will use a scalpel to make an incision up to ten inches to allow access to the organ.
What is laparoscopic surgery?
Also known as keyhole surgery, band-aid surgery, diagnostic laparoscopy, and minimally invasive surgery, laparoscopy is a small incision-initiated operation. It is less painful than other surgeries and is usually used to diagnose and treat organs in the pelvic or abdominal region.
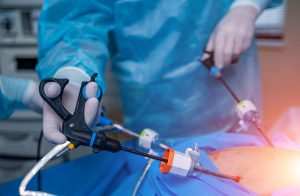
Difference between open surgery and laparoscopic surgery !?
The main difference between open surgery and laparoscopic surgery is the size of the incision. Open surgery is a traditional procedure in which a single incision is made, several inches long, if not more, to access the abdomen.
In contrast, laparoscopic surgery is a minimally invasive operation that uses several incisions of a quarter or less. Here, the surgeon uses a special laparoscope tool to help perform procedures using very small incisions. Laparoscopy uses more advanced techniques compared to open surgery. Hence, many people prefer laparoscopy to open surgery.
In addition, the individual needs more time to recover from open surgery than from laparoscopy. According to reports, the laparoscopic approach generally causes less blood loss, and less trauma, and provides faster recovery with reduced hospitalization compared to open surgery.
However, laparoscopy requires general anesthesia and costs more than open surgery. There are also certain restrictions for people with medical conditions such as heart disease, obesity, etc. while open surgery costs less and can be performed under local anesthesia while the patient is awake. However, it can cause longer hospital stays, larger scars, more pain, and a higher risk of complications such as infection and bleeding.
With increasing public awareness and growing advances in minimally accessible surgery, one of the most frequently asked questions by people is whether they should go for open or laparoscopic surgery. In most cases, a minimally invasive approach may not be feasible, and open surgery may have a better outcome.
However, sometimes the opposite can be true. Nowadays, many surgeons prefer laparoscopic surgery because it is faster and more advanced. However, you should always consult your doctor to know the benefits and risks of each surgery before making your choice.
Surgery is a major life event that will change your future for the better. However, there are certain prices that have to be paid for this. Both open surgery and laparoscopic surgery have their pros and cons. Therefore, when deciding what surgery you want to go for, keep in mind the cost and recovery period.